ProtaStructure Design Guide – Pad Footing Design to TS500
Summary
Revised Content with Transition Words
Pad Footing Design in Accordance with TS500
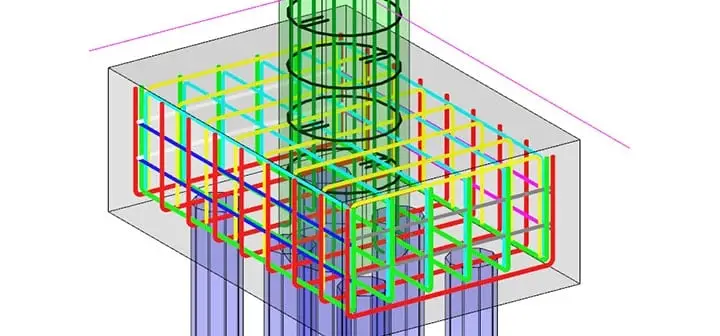
Pad footings are among the simplest and most widely used foundation types in structural engineering. They effectively transfer column loads to the soil, ensuring stability and preventing settlement or bearing failure. This document explains the process of designing a pad footing in compliance with TS500, the Turkish Standard for Reinforced Concrete Structures.
To make the design process clear, an example pad footing is selected and analyzed under a single load combination. By following a step-by-step approach, engineers can understand the methodology, covering everything from load analysis to structural safety checks and compliance with TS500 guidelines.
Key Steps in Pad Footing Design According to TS500
Define the Design Parameters
First, it is essential to identify the column dimensions, applied loads, and soil bearing capacity. Additionally, engineers must specify the material properties for concrete and reinforcement steel to ensure accurate calculations.
Load Analysis
Next, a single load combination, including axial loads and moments, is applied to represent realistic conditions. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for all subsequent calculations.
Footing Dimensions
After determining the loads, the required area of the footing is calculated based on the column load and the allowable soil bearing pressure. Furthermore, the footing thickness is determined to resist punching shear and bending moments effectively.
Reinforcement Design
Then, the main reinforcement is designed to handle bending moments. If required, shear reinforcement is provided based on punching and one-way shear checks to ensure structural integrity.
Code Compliance Checks
Finally, it is critical to verify that the design meets TS500 requirements. These checks include ensuring adequate soil pressure, shear resistance, and proper reinforcement placement.
Numerical Example of Pad Footing Design
For instance, consider a square pad footing designed for a column carrying a 500 kN axial load and a 50 kNm moment. The footing is sized to ensure adequate bearing pressure distribution, while checks for punching shear and bending resistance are conducted. Moreover, the reinforcement detailing is completed in accordance with TS500 criteria, ensuring both safety and cost-effectiveness.
Real-World Applications
Pad footings play a vital role in various projects, from small residential structures to large industrial facilities. For example, engineers have successfully used ProtaStructure to design pad footings for complex projects. To see real-world structures modeled with ProtaStructure, visit our Project Gallery.
Moreover, our Customer Success Stories highlight how engineers worldwide utilize ProtaStructure for efficient and accurate pad footing design. These stories demonstrate how ProtaStructure ensures compliance and safety across diverse structural projects.
Why Accurate Pad Footing Design Matters
Accurate pad footing design is essential to create stable and durable foundations. By following TS500 guidelines, engineers can minimize risks of settlement and failure. Furthermore, compliance with local standards ensures structural efficiency and promotes safety throughout the building’s lifecycle.







